Forced breathing during exhalation involves contraction of the internal intercostal muscles and the
A) scalenes.
B) diaphragm.
C) abdominal muscles.
D) external intercostals.
E) serratus anterior.
C) abdominal muscles.
You might also like to view...
The principal cation in intracellular fluid is
A) sodium. B) potassium. C) calcium. D) magnesium. E) chloride.
Myoglobin is a molecule within muscle cells that can bind
A. creatine phosphate. B. oxygen. C. hemoglobin. D. acetylcholine. E. ATP.
Using the figure below, identify the labeled part.
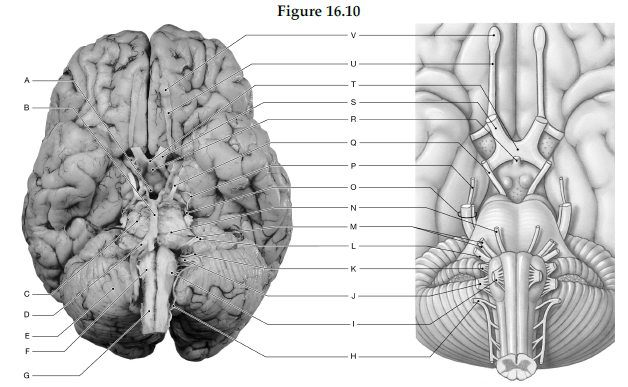
1) Label A: ______________________________
2) Label B: ______________________________
3) Label C: ______________________________
4) Label D: ______________________________
5) Label E: ______________________________
6) Label F: ______________________________
7) Label G: ______________________________
8) Label H: ______________________________
9) Label I: ______________________________
10) Label J: ______________________________
11) Label K: ______________________________
12) Label L: ______________________________
13) Label M: ______________________________
14) Label N: ______________________________
15) Label O: ______________________________
16) Label P: ______________________________
17) Label Q: ______________________________
18) Label R: ______________________________
19) Label S: ______________________________
20) Label T: ______________________________
21) Label U: ______________________________
22) Label V: ______________________________
Blood leaves the ________ and enters the glomerulus.
A) efferent arteriole B) peritubular capillary C) afferent arteriole D) Bowman's capsule E) vasa recta