Which of the following types of galaxies are typically reddest in color?
A) spirals
B) ellipticals
C) irregulars
B) ellipticals
You might also like to view...
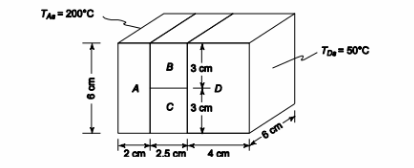
A section of a composite wall with the dimensions shown below has uniform temperatures of 200°C and 50°C over the left and right surfaces, respectively. If the thermal conductivities of the wall materials are: kA = 70 W/(m K), kB = 60 W/(m K), kc = 40 W/(m K) and kD = 20 W/(m K), determine the rate of heat transfer through this section of the wall and the temperatures at the interfaces. including a contact resistance of 0.1 K/W at each of the interfaces.
GIVEN
• Composite wall
• Thermal conductivities:
? kA = 70 W/(m K)
? kB = 60 W/(m K)
? kC = 40 W/(m K)
? kD = 20 W/(m K)
• Surface temperatures
? Left side (TAs) = 200°C
? Right side (TDs) = 50°C
• Contact resistance at each interface (Ri) = 0.1 K/W FIND
(a) Rate of heat transfer through the wall (q) (b) Temperatures at the interfaces
ASSUMPTIONS
• One dimensional conduction
• The system is in steady state
SKETCH
Mercury's evolution was different from the Moon's because:
A) Mercury developed a dense atmosphere while the Moon never did. B) Mercury was located farther from Earth, so experienced no tidal forces. C) Mercury was subject to more intense asteroid bombardment than the Moon. D) dense Mercury had an iron core that shrank, creating the lobate scarps. E) Mercury developed a strong magnetic field to protect it from solar radiation.
The heaviest nuclei of all are formed
A) in the horizontal branch. B) in dense white dwarfs. C) during nova explosions. D) in the ejection of matter in the planetary nebula. E) in the core collapse that set the stage of Type II supernovae.
The theory proposing light as a particle is supported by
1.the sparks created in Hertz' experiment with the spark gap oscillator. 2.the speed of light turning up in Maxwell's equations. 3.the interference caused by light in Young's double slit experiment. 4.the photoelectric effect Hertz discovered.