What is a Bénard cell?
What will be an ideal response?
In free convection on horizontal surfaces the fluid above the surface,
particularly if the surface has a higher temperature than the fluid, the fluid will
rise and cool down. This action results in the fluid circulating in a “cell”,
returning to the hot surface to be reheated and continuing. These cells have
been observed and measured to some extent. More work and study could be
done with this subject.
You might also like to view...
A v vs. t graph is drawn for a ball moving in one direction. The graph starts at the origin and at t = 5 s the acceleration of the ball is zero. We know that at t = 5 s,
a. the slope of the curve is non-zero. b. the velocity of the ball is not changing. c. the curve is not crossing the time axis. d. the curve is at v = 0, t = 0.
Emission nebulae are also called _____
A) dark nebulae B) H II regions C) reflection nebulae D) N II regions
Ideal Gas Law: As shown in the figure, an air pocket at the top of a vertical tube, closed at the upper end and open at the lower, occupies a volume of 560 cm3 at the surface of a lake where the air pressure is 1.0 × 105 Pa and the temperature is 37°C. What is the volume of the air in the pocket if the tube is taken to a depth of 56 meters, where the temperature is 7°C? Assume that none of the air escapes from the tube. The density of the water in the lake is 1000 kg/m3.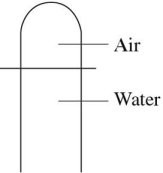
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
According to this graph, a planet with 10 times the mass of Jupiter would have a radius about ________ as that of Jupiter.
A) the same B) 10 times as large C) 100 times as large D) 60% as large