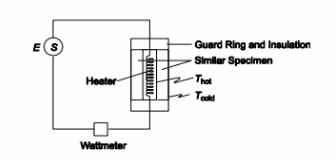
To measure thermal conductivity, two similar 1-cm-thick specimens are placed in an apparatus shown in the accompanying sketch. Electric current is supplied to the 6-cm by 6-cm guarded heater, and a wattmeter shows that the power dissipation is 10 watts (W). Thermocouples attached to the warmer and to the cooler surfaces show temperatures of 322 and 300 K, respectively. Calculate the thermal conductivity of the material at the mean temperature in W/(m K).
GIVEN
Thermal conductivity measurement apparatus with two samples as shown
Sample thickness (L) = 1 cm = 0.01 cm
Area = 6 cm ? 6 cm = 36 cm2 = 0.0036 m2
Power dissipation rate of the heater (qh) = 10 W
Surface temperatures
Thot = 322 K
Tcold = 300 K
FIND
The thermal conductivity of the sample at the mean temperature in W/(m K)
ASSUMPTIONS
One dimensional, steady state conduction
No heat loss from the edges of the apparatus
SKETCH
By conservation of energy, the heat loss through the two specimens must equal the power dissipation
of the heater. Therefore the heat transfer through one of the specimens is qh/2.
For one dimensional, steady state conduction.
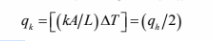
Solving for the thermal conductivity
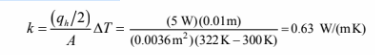
You might also like to view...
When you document the time and place of a meteorite as it streams through the atmosphere, it is considered a(n) ____
a. fall b. find c. meteoroid d. chondrite e. impactor
A particle moving with a constant acceleration has a velocity of 20 cm/s when its position is x = 10 cm. Its position 7.0 s later is x = ?30 cm. What is the acceleration of the particle?
a. ?7.3 cm/s2 b. ?8.9 cm/s2 c. ?11 cm/s2 d. ?15 cm/s2 e. ?13 cm/s2
Two sources emit beams of light of wavelength 550 nm. The light from source A has an intensity of 10 µW/m2, and the light from source B has an intensity of 20 µW/m2. This is all we know about the two beams
Which of the following statements about these beams are correct? (There could be more than one correct choice.) A) Beam B carries twice as many photons per second as beam A. B) A photon in beam B has twice the energy of a photon in beam A. C) The frequency of the light in beam B is twice as great as the frequency of the light in beam A. D) A photon in beam B has the same energy as a photon in beam A. E) None of the above statements are true.
Sirius, the brightest star in the sky, is 8.7 ly from the Sun. Determine Sirius' declination and right ascension