How does the Kepler mission plan to detect Earth-like planets around other stars?
A) by measuring the Doppler shift in spectral lines as the central star is tugged to and fro by the planet
B) by observing the slight dip in brightness of the central star as the planet transits
C) by directly imaging the planet
D) by observing the spectrum of the planet
E) by measuring the slight shift in position of the central star as it is tugged to and fro by the planet
B
You might also like to view...
An constant electric field, 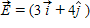
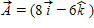
src="https://sciemce.com/media/2/ppg__cognero__Chapter_25_Gauss_apos_s_Law.__media__7d94a3f5-3b36-4dc7-aedd-c86064e2bc84.PNG" style="vertical-align:middle;" />. What is the magnitude of the electric flux through this area? A. 24 N ? m2/C B. 48 N ? m2/C C. 0.24 N ? m2/C D. 0.48 N ? m2/C E. 0
The elastic modulus of a material, except for elastomers, is proportional to the _____________of the interatomic potential.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Explain the meaning of temperature
A 5,000 kg satellite is orbiting the Earth in a circular path. The height of the satellite above the surface of the Earth is 800 km. The velocity of the satellite is 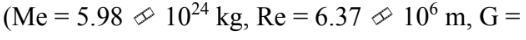
A. 7,460 m/s. B. 6,830 m/s. C. 6,430 m/s. D. 5,950 m/s. E. 5,350 m/s.