The long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm is to the left of the low point on its average total cost curve.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
True
You might also like to view...
When your grandfather keeps a bundle of $100 dollar bills behind a brick in the basement, this is an example of dollars serving as:
A. a store of value. B. a medium of exchange. C. bank reserves. D. a unit of account.
Slick Shades has a constant marginal cost of production equal to $80 and the distributors have a constant marginal cost of distribution equal to $30. If Slick Shades is producing the profit-maximizing number of sunglasses (in hundreds) and charging the profit-maximizing wholesale price, what is the retail price?
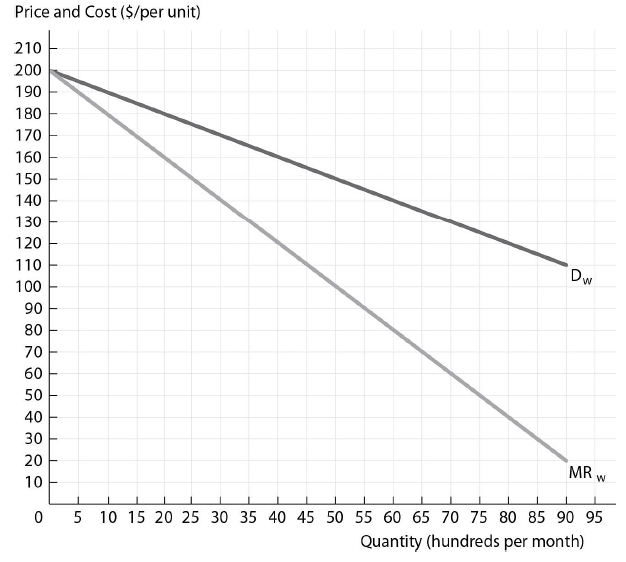
The figure above shows the wholesale demand and marginal revenue curves for Slick Shades Sunglasses, a sunglasses firm with market power. Slick Shades Sunglasses has a constant marginal cost of production and it sells to perfectly competitive independent retail distributors that have a constant marginal cost of distribution.
A) $180
B) $170
C) $160
D) $200
If the equilibrium price of widgets is $22, and then a price ceiling of $24 is imposed by the government, as a result,
a. there will be no effect on the widget market.
b. there will be a shortage of widgets
c. there will be a surplus of widgets.
d. the price of widgets will increase.
Price equals the minimum of long-run average cost
A. in a short-run equilibrium as well as in a long-run equilibrium. B. in a long-run equilibrium. C. whenever average revenue equals marginal cost. D. along a horizontal long-run supply curve, but not along an upward sloping long-run supply curve.