Your bike is worth $100 and if you park it outside at school there is a 25% chance that it will be stolen. Your utility function for money is U = 100(M). Assume throughout that the bike value and money are interchangeable since you could sell the bike instantly at its value if necessary. Are you risk averse, a risk lover, or risk neutral?
What will be an ideal response?
Risk neutral since your marginal utility of money is constant.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as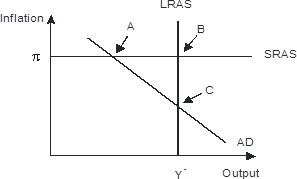
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
Use the data in the table below to answer the following question.PriceQuantity Demanded$201218171620142412301036840644448The price elasticity of demand (based on the midpoint formula) when price decreases from $12 to $10 is
A. inelastic. B. unit elastic. C. elastic. D. perfectly elastic.
Over the range of diminishing marginal product, if the variable input to a firm is increased: a. output will increase more than in proportion to the increase in the input
b. output will increase less than in proportion to the increase in the input. c. output will increase exactly in proportion to the increase in the input. d. output will increase more than in proportion to the increase in the inputs at first, but it will eventually increase less than in proportion to the increase in the input.
An increase in the money supply shifts the aggregate-supply curve to the right
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false