If a foreign supplier sells a good in another country at a cheaper price than it sells the good in its home market, the
a. foreign supplier will gain a monopoly in the foreign market.
b. consumers in the receiving country will be harmed by the dumping of the good into its domestic market.
c. consumers in the receiving country can gain from buying the foreign-produced good if it is cheaper than the cost of producing the good domestically.
d. usual implications of the law of comparative advantage with trade restrictions do not hold in this case, particularly if the low-cost supplier is subsidized by a foreign government.
C
You might also like to view...
Which of the following always decreases when output increases?
A) total fixed cost B) marginal cost C) average variable cost D) average fixed cost E) total cost
Suppose the country of Popcorn produces only jets and corn. If Popcorn cannot produce any more jets without giving up corn, we say that Popcorn has achieved
A) the highest marginal benefit. B) production efficiency. C) the lowest marginal cost. D) the highest opportunity cost.
The type of unemployment created by the normal rate of reentry and entry into the labor force is
A) frictional unemployment. B) structural unemployment. C) cyclical unemployment. D) seasonal unemployment.
Refer to the following graph. At which of the following prices will the firm be losing money but should remain in operation?
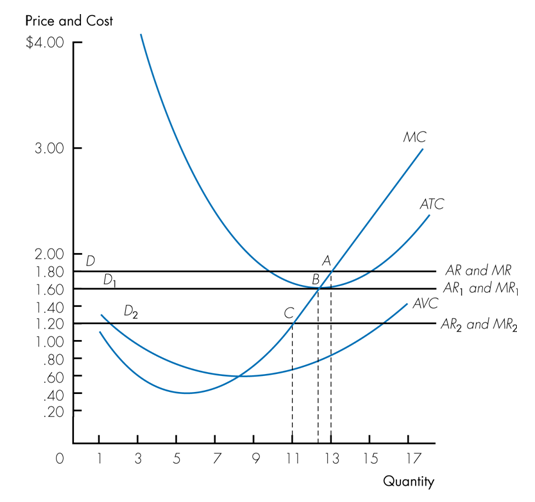
a. $1.80
b. $1.60
c. $1.20
d. $0.40