Consider the following approach for testing whether a classifier A beats an- other classifier B. Let N be the size of a given data set, pA be the accuracy of classifier A, pB be the accuracy of classifier B, and p = (pA + pB)/2 be the average accuracy for both classifiers. To test whether classifier A is significantly better than B, the following Z-statistic is used:
![]()
Classifier A is assumed to be better than classifier B if Z > 1.96.
Table 4.3 compares the accuracies of three different classifiers, decision tree
classifiers, na ??ve Bayes classifiers, and support vector machines, on various
data sets. (The latter two classifiers are described in Chapter 5.)
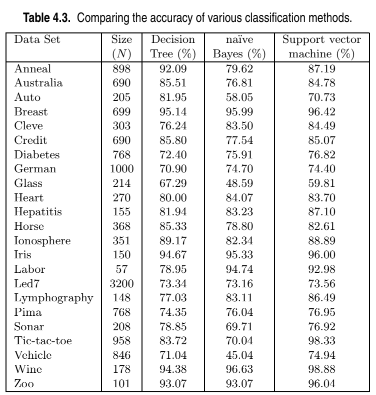
A summary of the relative performance of the classifiers is given below:
You might also like to view...
Answer the following questions true (T) or false (F)
1. The method clone has one parameter and should return a copy of the calling object. 2. An abstract class is a class that has some methods without complete definitions.
C-strings can be manipulated by using either standard library functions or as subscripted array variables.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
The _____ sheet button allows you to add worksheets to a workbook.?
A. ?Blank B. ?New C. Create D. ?Add
A linked list is an ordered collection of data in which each element contains the location of the next element or elements.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)