The figure below shows an IS-LM-FE model for an economy with fixed exchange rates. Initially the economy was at Point A, a triple intersection. Here, the FE curve is flatter than the LM curve.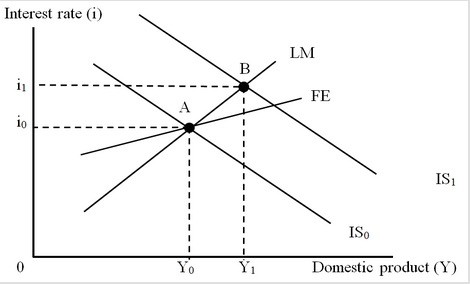 Assume that the economy was initially at Point A. Which of the following would have caused the economy to move to and remain at Point B?
Assume that the economy was initially at Point A. Which of the following would have caused the economy to move to and remain at Point B?
A. Expansionary monetary policy with sterilization
B. Expansionary monetary policy without sterilization
C. Contractionary fiscal policy without sterilization
D. Expansionary fiscal policy with sterilization
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is explained by the law of diminishing marginal utility?
A) The marginal utility of Isabel's second bottle of Coca-Cola is greater than the marginal utility of her friend Margie's third pretzel. B) The marginal utility of Isabel's second bottle of Coca-Cola is greater than the marginal utility of her third pretzel. C) The total utility of one bottle of Coca-Cola is greater than the total utility of two bottles of Coca-Cola. D) The marginal utility of Isabel's second bottle of Coca-Cola is greater than the marginal utility of her third bottle of Coca-Cola.
Generally, positive externalities result in
A. too much of a good being produced. B. the socially optimal output of a good being produced. C. too little of a good being produced. D. either a or c E. any of the above
A monopoly firm is a ______________ and faces a __________ sloping demand curve
a. Price taker; horizontal b. Price searcher; horizontal c. Price searcher; downward d. Price taker; downward
Aggressive policy measures taken by the monetary authority during the 2007-2008 financial crisis in the United States resulted in:
a. avoidance of a recession caused by a tight credit market. b. almost no transmission of the monetary stimulus to market rates of interest, increased lending, and expansion of GDP. c. lower rates of interest and increased investment activity. d. an increase of real GDP and a fall in the core unemployment rate.