In the AS/AD model, an effect of an expansionary monetary policy is to:
A. shift the aggregate demand curve to the left.
B. reduce investment spending.
C. raise interest rates.
D. lower interest rates.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Employing Figure 4-1 above, if Y increases by 3000 and the interest rate is fixed at 5% then the sensitivity of real money balances to changes in real income is
A) 0.67. B) 0.33. C) -0.67. D) -0.33.
A monopoly faces an inverse demand curve of P = 100 - 2Q. The marginal cost curve is MC = .5Q. What government price ceiling would represent optimal price regulation?
What will be an ideal response?
If nations erect tariffs and quotas to restrict trade, what is likely to happen to predicted values of currencies drawn from the purchasing power parity theory?
a. They will be understated for tariffs and overstated for quotas. b. They will be overstated for tariffs and understated for quotas. c. They will be the correct values. d. They will be incorrect.
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD3 the result in the short run would be: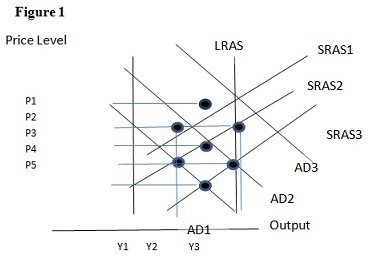
A. P1 and Y2. B. P2 and Y3. C. P3 and Y1. D. P2 and Y2.