A 2.3-kg object traveling at 6.1 m/s collides head-on with a 3.5-kg object traveling in the opposite direction at 4.8 m/s
If the collision is perfectly elastic, what is the final speed of the 2.3-kg object?
A) 0.48 m/s
B) 7.1 m/s
C) 3.8 m/s
D) 4.3 m/s
E) 6.6 m/s
B
You might also like to view...
As a system loses the ability to do work, its entropy decreases
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Stan argues that momentum cannot be conserved when a collision is not a head-on collision. Rachel insists it is conserved because each body receives an impulse of equal magnitude. Rachel is correct because
a. each body exerts an equal and opposite force on the other during the collision. b. the forces act during equal time intervals. c. the law of conservation of momentum for an isolated system is a vector equation. d. of all of the above. e. of only (a) and (b) above.
Orbital Angular Momentum: What is the greatest magnitude of the orbital angular momentum L that you can find in a state with n = 6?
A. 5.48 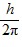
B. 5.92 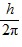
C. 6 
D. 6.48 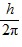
As global warming progresses, the
A) landmasses will warm the most B) equatorial regions will warm the most C) polar regions will warm the most D) oceans will warm the most