The sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the ANS differ in the
A. length of the preganglionic and postganglionic axons.
B. location of the preganglionic cell bodies.
C. position of the ganglia where preganglionic and postganglionic neurons synapse.
D. length of the preganglionic and postganglionic axons, and location of the preganglionic cell bodies.
E. length of the preganglionic and postganglionic axons, location of the preganglionic cell bodies, and position of the ganglia where preganglionic and postganglionic neurons synapse.
E
You might also like to view...
Using Figure 7.1, match the following:
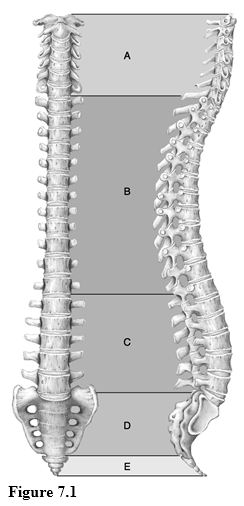
1) Articulates with hip bones of the pelvis.
2) Attach to ribs.
3) Receive the most stress.
4) Transverse foramina present.
5) No canals or foramen present.
6) Includes the atlas and the axis.
7) Contains the joint that allows you to rotate your head "no."
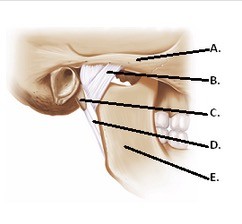 The figure illustrates structures in the right temporomandibular joint (lateral view). What does "D" represent?
The figure illustrates structures in the right temporomandibular joint (lateral view). What does "D" represent?
A. Styloid process B. Zygomatic arch C. Lateral ligament D. Stylomandibular ligament E. Mandible
The region beneath the free edge of the nail is called the ________
A) hyponychium B) lunule C) eponychium D) nail bed
Second-order neurons synapse with third-order neurons in the ________
A) spinal cord B) cerebral cortex C) dorsal root ganglion D) thalamus E) medulla oblongata