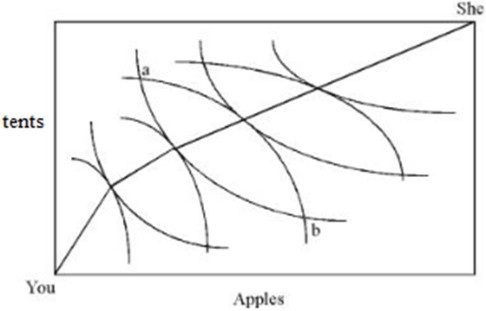
Sketch a typical consumption contract curve in an Edgeworth box for you and her. The two products should be apples and tents. Identify two consumption baskets where you and she are off the contract curve. Label the first point (a) where you value apples much more than she does; label the second point (b) where you value apples much less than she does.
What will be an ideal response?
You might also like to view...
Which of the following equations does NOT state a condition required for equilibrium output:?
A) Y = C(Yd) + I + G + CA(EP*/P,Yd) B) Y = C(Y - T) + I + G + CA(EP*/P,Y - T) C) Y = D(EP*/P,Y - T,I,G) D) R = R* + (EP/E) E) Y = D(EP*/P,Yd,I,G)
Although the U. S. airline industry has only a relatively small number of sellers, the market is nevertheless highly competitive. The reason is that:
A) the number of buyers is very large. B) due to fierce competition, no firm has significant control over prices. C) due to fierce competition, no firm has significant control over the quantity supplied. D) most airline routes are served by relatively many sellers.
In a perfectly competitive market, the process of entry and exit will end when
a. price equals minimum marginal cost. b. marginal revenue equals marginal cost. c. economic profits are zero. d. accounting profits are zero.
Imagine the U.S. economy is in long-run equilibrium. Then suppose the value of the U.S. dollar decreases. At the same time, people in the U.S. revise their expectations so that the expected price level rises. We would expect that in the short-run
a. real GDP will rise and the price level might rise, fall, or stay the same.
b. real GDP will fall and the price level might rise, fall, or stay the same.
c. the price level will rise, and real GDP might rise, fall, or stay the same.
d. the price level will fall, and real GDP might rise, fall, or stay the same.