Based on the graph for saving incentives, a tax law change encouraging saving would ______.
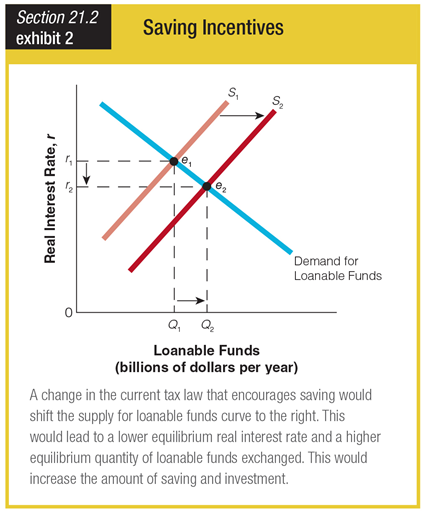
a. create a higher equilibrium quantity of loanable funds exchanged
b. create a lower equilibrium quantity of loanable funds exchanged
c. have no influence on the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds exchanged
d. drive the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds exchanged to zero
a. create a higher equilibrium quantity of loanable funds exchanged
You might also like to view...
Most natural monopolies are regulated at some level by a government because:
a. an unregulated natural monopolist would cause the problem of capital outflow. b. an unregulated natural monopolist would produce only for government bureaucrats. c. an unregulated natural monopolist would charge an inefficiently low price in the market. d. an unregulated natural monopolist would charge an inefficiently high price in the market. e. an unregulated natural monopolist would incur losses.
The short run is the time period during which
a. all of the firm's costs are fixed. b. the value of the firm's assets starts to decay. c. the firm can adjust all inputs freely. d. some of the firm's input decisions are constrained by previous commitments.
The relationship between industrial capacity percentage and
a. the unemployment rate is indirect. b. the unemployment rate is direct. c. real GDP is indirect. d. nominal GDP is indirect.
Which of the following is true?
A) Most stockholders own stock because they want to run the business. B) The shareholders of a large well-established firm are guaranteed to earn a real rate of return of about seven percent in the future. C) Ownership of a corporate bond provides the bondholder with an ownership right to a fraction of the firm's future profits. D) Stock ownership makes it possible for investors to own a fractional share of a firm's future profits even if they do not participate in the operation of the firm.