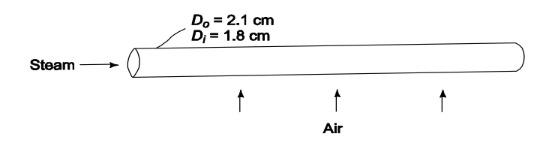
In a heat exchanger, as shown in accompanying figure, air flows over brass tubes of 1.8- cm-ID and 2.1-cm-OD that contain steam. The convection heat-transfer coefficients on the air and steam sides of the tubes are 70 W/(m2 K) and 210 W/(m2 K), respectively. Calculate the overall heat transfer coefficient for the heat exchanger (a) based on the inner tube area, (b) based on the outer tube area but assume that a fouling factor of 0.00018 (m2 K)/W has developed on the inside of the tube during operation.
GIVEN
• Air flow over brass tube containing steam
• Tube diameters Inside (Di) = 1.8 cm = 0.018 m
Outside (Do) = 2.1 cm = 0.021 m
• Convective heat transfer coefficients Air side h o= 70 W/(m2 K)
Steam side h i= 210 W/(m2 K)
• Fouling factor on the inside of the tube (Rd) = 0.0018 (m2 K)/W
FIND
• The overall heat transfer coefficient for the heat exchanger based on
(a) the inner tube area (Ui) and (b) the outer tube area (Uo)
ASSUMPTIONS
• The heat transfer coefficients are uniform over the transfer surfaces
SKETCH
From the solution to

without fouling. The overall heat transfer coefficient with fouling (Ud) can be calculated by rearranging
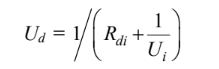
(a) Based on the inner tube area
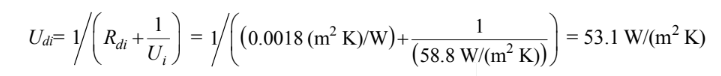
(b) To base the overall heat transfer coefficient on the outer tube area, the fouling factor must also be based on the outer tube area
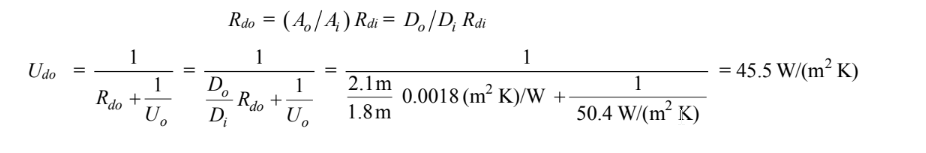
You might also like to view...
Mathematical models indicate that ____ galaxies are produced by high speed collisions in which a smaller galaxy passes through another galaxy almost perpendicular to the disk of the galaxy
a. ring b. spiral c. antenna d. irregular e. tidal tail
If we could put all the asteroids together, their total mass would be ________
A) about the mass of Mercury B) about the mass of Earth C) greater than the mass of Earth but less than the mass of Jupiter D) much less than the mass of any terrestrial planet
A 2.0-kg mass is projected vertically upward from ground level with an initial speed of 30 m/s. The mass rises to a maximum height of 35 m above ground level. What is the change in mechanical energy of the mass caused by air resistance between the point of projection and the point of maximum height?
a. ?0.21 kJ b. ?0.47 kJ c. ?0.40 kJ d. ?0.34 kJ e. ?0.69 kJ
Is film condensation more effective on vertical tubes or on horizontal tubes?
What will be an ideal response?