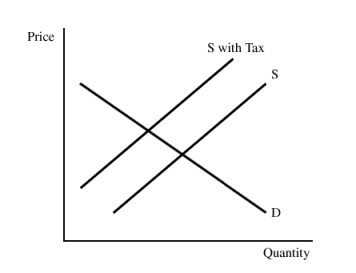
 Figure 16.4The pollution tax in Figure 16.4:
Figure 16.4The pollution tax in Figure 16.4:
A. increases equilibrium output.
B. internalizes the pollution externality.
C. increases supply.
D. All of these
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Increased United States military expenditures and action in response to the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001 suggest that military officials in the United States _____
a. could not wait to go to war b. view the War on Terror as a negative externality c. believe that military expenditures can act as a deterrent d. are incompetent
Representative money is
a. accepted on faith. b. found in M1 and M2 money measures. c. today in the form of check able deposits. d. redeemable for a commodity.
Which of the following is true? a. The private market provides too much of goods that generate external benefits
b. In the case of external benefits, if we could add the benefits that are derived by non-paying consumers, the supply curve would shift to the right, increasing output. c. In the case of external benefits, a tax equal to external benefits would result in an efficient level of output. d. In the case of public goods, when people act as free-riders, some goods having benefits greater than costs will not be produced.
Suppose that indifference curve I1 lies to the right of indifference curve I2. We can conclude that
A. all points along indifference curve I1 will correspond to lower utility than points along indifference curve I2. B. some, but not all, points on indifference curve I1 will correspond to lower utility than points along indifference curve I2. C. all points along indifference curve I1 will correspond to higher utility than points along indifference curve I2. D. some, but not all, points on indifference curve I1 will correspond to higher utility than points along indifference curve I2.