What is the U.N.'s goal for foreign aid to poor countries? Are most countries currently meeting this goal? Explain.
What will be an ideal response?
The U.N.'s Millennium Aid Goal is to raise foreign aid to 0.7 percent of donor country GDP. Currently most rich nations are not meeting the goal. The average contribution for developed countries is 0.29 percent of GDP. The United States, the United Kingdom, Japan and others contribute billions of dollars in aid each year, yet they are well below the goal set by the U.N. However, Denmark is a nation where donor country GDP exceeds the percentage set by the U.N.
You might also like to view...
Suppose the quantity demanded is 5 units when the price is $1.00. If the price rises to $2.00, the quantity demanded falls to 3 units. The price elasticity of demand is
A) 0.5. B) 0.75. C) 1.33. D) 2.00.
The main difference between a sterilized intervention and unsterilized intervention in the foreign exchange market is:
A) a sterilized intervention is coordinated with other nations B) an unsterilized intervention does not change the exchange rate C) an unsterilized intervention does not change the monetary base D) a sterilized intervention does not change the monetary base
Dumping is said to occur when
A. Foreign producers sell their goods abroad at prices lower than our average cost of production. B. Foreign producers sell their goods abroad at prices lower than their marginal cost of production. C. Some foreign countries have trade surpluses and others have a trade deficit. D. Foreign producers sell their goods in export markets at prices below domestic prices.
Use the following figure showing the domestic demand and supply curves for product B in a hypothetical economy to answer the next question.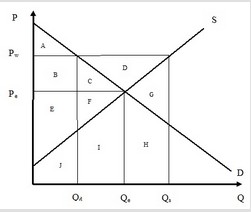 After trade, at a world price of Pw, total economic surplus equals area(s)
After trade, at a world price of Pw, total economic surplus equals area(s)
A. A + B + C + D + E + F. B. A + B + C + E + F + J + I. C. D. D. A + B + C + D.