What occurs during nuclear fusion within the Sun and how much energy is produced?
What will be an ideal response?
The fusion of hydrogen into helium in the Sun proceeds in three steps known as the proton–proton chain. The first step in the chain combines two hydrogen nuclei to produce a heavy hydrogen nucleus called deuterium. The second step forms light helium, and the third step combines the light helium nuclei to form normal helium. During the process, positrons, neutrinos, and gamma rays are formed and energy is released as the particles fly away.
Fusion can occur only in the core of the Sun where temperatures are pressures are high enough. Because particles of like charge repel one other, high temperatures are needed to give particles high enough velocities to overcome this Coulomb barrier and fuse together. High densities are needed to provide large numbers of reactions.
Only a tiny fraction of the hydrogen atoms fuse into helium, and the nuclear reactions in the Sun are spread through a large volume in its core. Any single gram of matter produces only a little energy. A person of normal mass eating a normal diet produces about 3,000 times more heat per gram than the matter in the core of the Sun. Gram for gram, you are a much more efficient heat producer than the Sun. The Sun produces a lot of energy because it contains many grams of matter in its core.
You might also like to view...
Two stars both lie on the main sequence. Star X is spectral type A, while Star Y is spectral type G. Therefore, Star X is more massive than Star Y
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
In addition to being the second-largest moon in the solar system, Saturn's moon Titan, is
A) the only moon to have its own internal magnetic field B) the only moon to have its own atmosphere C) more geologically active than the Earth D) the only moon to show evidence for a subsurface ocean of water
The current shown flowing through each coil must be 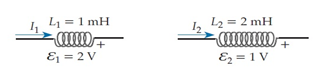
A. increasing. B. decreasing. C. remaining constant. D. One needs more information to say how it is varying.
This star map shows stars as we see them in our sky from Earth, centered around the constellation Canis Major. Larger dots represent brighter stars, and a few of the brightest stars are identified. From this view alone, what can you conclude about Sirius?
A) It has the greatest apparent brightness of any star in this region of the sky. B) It is the most luminous star in this region of the sky. C) It is the nearest star in this region of the sky. D) It is actually a binary star system in which the second star is a white dwarf. E) All of the above choices are true.