What is the wavelength of a 2.0-GeV electron?
A)
1.2 fm
B)
0.62 fm
C)
0.099 fm
D)
less than 10-18 m
E)
2 fm
B
You might also like to view...
Rotational Dynamics: A uniform solid cylinder of mass 10 kg can rotate about a frictionless axle through its center O, as shown in the cross-sectional view in the figure. A rope wrapped around the outer radius R1 = 1.0 m exerts a force of magnitude F1 = 5.0 N to the right. A second rope wrapped around another section of radius R2 = 0.50 m exerts a force of magnitude F2 = 6.0 N downward. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder?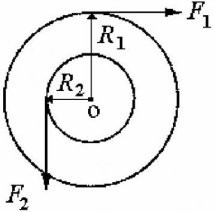
A. 1.0 rad/s2 B. 0.60 rad/s2 C. 0.40 rad/s2 D. 0.80 rad/s2
A substance that cools down faster than others has a
A) low specific heat capacity. B) high specific heat capacity. C) either of these D) neither of these
A 0.200-kg object, attached to a spring with spring constant k = 16.0 N/m, is moving on a horizontal frictionless surface in simple harmonic motion of amplitude of 0.0840 m. What is its speed at the instant when its displacement is 0.0420 m? (Hint: Use conservation of energy.)
a. 6.51 m/s b. 0.269 m/s c. 65.1 cm/s d. 84.0 cm/s e. 46.0 cm/s
Which of these is a likely source of strong gravity waves?
a. The Earth. b. The Sun. c. A supernova. d. Nuclear fission. e. Nuclear fusion in stars.