Using the above table, at a price of $70, there is
A) a surplus of 150 units.
B) a shortage of 120 units.
C) a surplus of 270 units.
D) a shortage of 150 units.
C
You might also like to view...
After graduation, you start an internet-based firm that allows people to buy and sell books online. Based on your market research, you believe there are two basic types of customers
The first type is the casual reader who has relatively low willingness-to-pay for your services, and their annual demand is Q1 = 30 - 40P where Q1 is the number of books traded per year and P is the price you charge per book traded. The second type of customer is the avid reader who has relatively high willingness-to-pay for your services, and their demand is Q2 = 100 - 50P. The marginal cost of your online service is $0.40 per book traded. a. If you set your usage fee equal to the marginal cost, how many books will each type of customer trade on your system? What is the consumer surplus enjoyed by each type of customer? b. What is the optimal entry fee that you should charge under a two-part tariff pricing scheme for access to your online market? How much consumer surplus is left for the two types of customers after they pay the entry fee and usage fee?
The price elasticity of demand for a rental home in Luxury Resorts in the summer is 1.25 and is 2.25 in the spring. If Luxury Resorts faces a constant marginal cost of $500 per home rental, what is the profit-maximizing peak-load price to charge in the summer?
A) $1,250 B) $5,000 C) $900 D) $2,500
If demand for a good is elastic, then the price elasticity will be:
A. equal to one. B. equal to zero. C. greater than one. D. less than one.
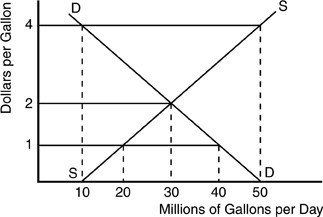 According to the above figure for a gasoline market, an increase in the price from $2 to $4 will result in
According to the above figure for a gasoline market, an increase in the price from $2 to $4 will result in
A. a shortage of 30 million gallons. B. an increase in quantity demanded of 10 million gallons. C. an increase in demand of 20 million gallons. D. an increase in quantity supplied of 20 million gallons.