To find an economy's long-run equilibrium price level, locate the point where ________ and ________ cross and look to the left
A) long-run aggregate supply; aggregate demand
B) aggregate demand; short-run aggregate supply
C) aggregate demand; price level
D) demand; supply
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
The concept of economies of scale becomes especially _____________ to international trade when it enables one or two large producers to supply the entire country.
a. problematic b. unrelated c. relevant d. unproductive
Refer to Table 3.2, which shows some costs and benefits of having your car repaired. What is the marginal cost of the 5th hour spent on repairs?
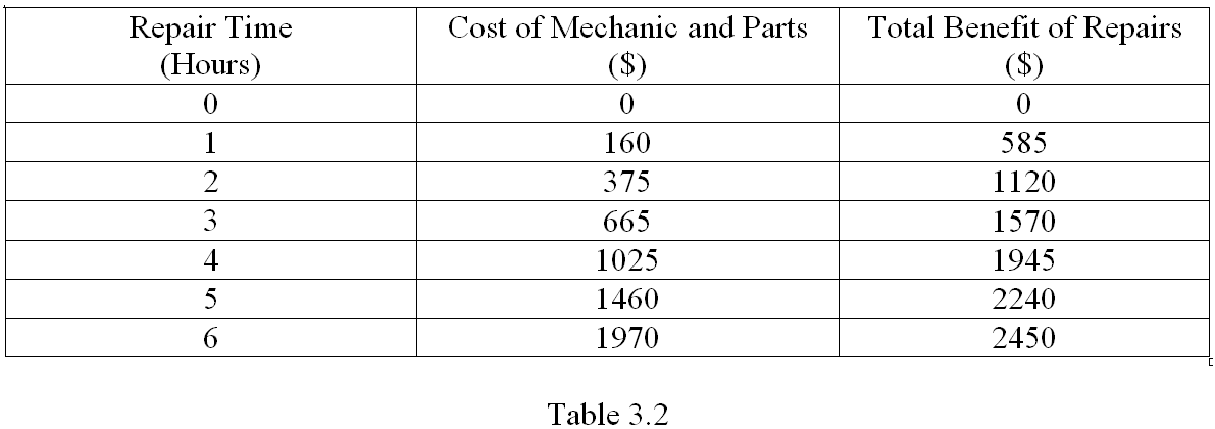
A. $360
B. $435
C. $510
D. $780
According to the liquidity preference theory, an increase in the overall price level of 10 percent
a. increases the equilibrium interest rate, which in turn decreases the quantity of goods and services demanded. b. decreases the equilibrium interest rate, which in turn increases the quantity of goods and services demanded. c. increases the quantity of money supplied by 10 percent, leaving the interest rate and the quantity of goods and services demanded unchanged. d. decreases the quantity of money demanded by 10 percent, leaving the interest rate and the quantity of goods and services demanded unchanged.
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a tax cut that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ and eventually to a long-run equilibrium at point ________, if left to self-correcting tendencies. 
A. D; C B. B; C C. B; A D. D; B