A medical test has been designed to detect the presence of a certain disease. Among those who have the disease, the probability that the disease will be detected by the test is 0.99. However, the probability that the test will erroneously indicate the presence of the disease in those who do not actually have it is 0.02. It is estimated that 7% of the population who take this test have the disease.
If necessary, round your answers to three decimal places.
If the test administered to an individual is positive, what is the probability that the person actually has the disease?
__________
If an individual takes the test twice and both times the test is positive, what is the probability that the person actually has
the disease?
__________
0.788; 0.995
You might also like to view...
Use the Gauss-Jordan method to find A-1, if it exists.A = 
A. 
B. 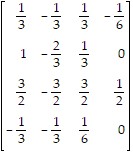
C. 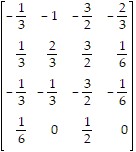
D. Does not exist
Provide an appropriate response.Multiply: (7)(4)(8)(3)
A. 756 B. 896 C. 22 D. 672
Solve.The pitch P of a musical tone varies inversely as its wavelength W. One tone has a pitch of 212 vibrations per second and a wavelength of 19.3 ft. Find the wavelength of another tone that has a pitch of 219 vibrations per second.
A. 18.7 ft B. 2405.6 ft C. 0.000416 ft D. 0.05 ft
Perform the indicated operation.5.859 - 5.397
A. 0.562 B. 0.462 C. 10.256 D. 11.256