Refer to the graph below. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is an unanticipated decrease in aggregate demand to AD2, then in the view of new classical economics the economy will:
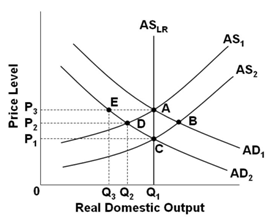
A. Self-correct through a shift in AS, which brings output back to Q1
B. Self-correct through a shift in AD, which brings output back to Q1
C. Need the government to implement expansionary policy in order to bring output back to Q1
D. Need the government to implement contractionary policy in order to bring output back to Q1
A. Self-correct through a shift in AS, which brings output back to Q1
You might also like to view...
Suppose y is measured on the vertical axis, x is on the horizontal axis, and the various combinations of x and y are shown by a nonvertical straight line. Which of the following must be true?
a. There is a negative relation between x and y. b. There is a positive relation between x and y. c. There is a causal relation between x and y. d. If the value of x is known, the value of y can be determined. e. The value of y is independent of the value of x.
Explain the difference between inferior and normal goods. As a developing economy experiences increases in income (measured by GDP), what would you predict to happen to demand for inferior goods?
When policy makers choose between tax policy and spending policy to affect the level of aggregate demand, they tend to choose on the basis of
A. how large a public sector they want. B. how much they want to change aggregate demand. C. how much they want to change aggregate supply. D. which has the larger multiplier.
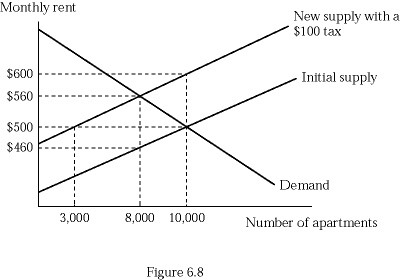 Refer to Figure 6.8. If your city imposes a tax of $100 per apartment, the tax would incur the deadweight loss of:
Refer to Figure 6.8. If your city imposes a tax of $100 per apartment, the tax would incur the deadweight loss of:
A. $48,000. B. $100,000. C. $520,000. D. $560,000.