Figure 9-11 illustrates the long-run average total cost curve for a perfectly competitive firm and the short-run average total cost curve (ATC*) for the firm’s current plant size. In the long run, this
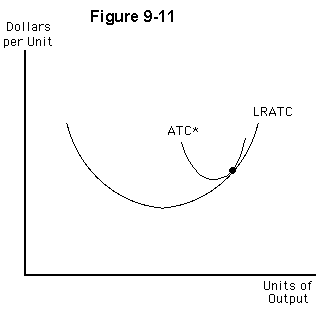
a.
firm's plant size is too large to allow it to earn a normal profit
b.
firm's plant size is too small to allow it to earn a normal profit
c.
firm will be able to stay in operation with the same plant size
d.
firm will suffer an economic loss
e.
firm will earn an economic profit
a
You might also like to view...
Double counting occurs when:
A) inputs are included in the calculation of the gross domestic product. B) household production is included in the calculation of the gross domestic product. C) depreciation is included in the calculation of the gross domestic product. D) unsold inventories are included in the calculation of the gross domestic product.
In the above figure, what would be the profit or loss at the marginal cost pricing point for this natural monopolist?
A) -$300 B) $2,700 C) $2,100 D) -$1,200
In the United States, a cup of hot chocolate costs $5 . In a foreign country, the same hot chocolate costs 6.5 units of that country's currency. If the exchange rate were 1.3 units of foreign currency per U.S. dollar, what is the real exchange rate?
a. 1/2 cup of that country's hot chocolate per cup of U.S. hot chocolate b. 1 cup of that country's hot chocolate per cup of U.S. hot chocolate c. 2 cups of that country's hot chocolate per cup of U.S. hot chocolate d. None of the above is correct.
Which of the following is an example of a progressive tax?
A. A local sales tax. B. An excise tax. C. The federal income tax. D. Social Security payroll tax.