Excimer laser radiation from KrF 248 nanometer (nm) broad beam can produce ozone from air.(76) Discuss whether the lofting of low-level satellites containing excimer lasers could be used to restore the ozone layer
What will be an ideal response?
This would be possible, but extremely expensive to accomplish. Each satellite
launch would be expensive in itself, and because the satellite would be in low Earth orbit, air
resistance (though not large) would cause the orbit to decay. Either there would have to be
provision for continuous orbit correction (the satellites would need to carry extra fuel to
correct the orbit) or the satellites would fall to Earth after a short time and have to be
replaced. Neither option seems very cost effective.
Then there is the problem of supplying power to the laser. Perhaps solar energy could be
used, but then the question of the amount of energy needed. It will be perhaps obvious that
to get sufficient ozone formation would require substantial power expenditure, and require a
very large area of solar panels. The greater the weight lofted by a rocket, the more expensive
the launch in fuel.
This overall, while possible technically, seems unlikely to solve the problem at reasonable
cost.
While I would not expect this detailed an answer from a student, I would expect students to
recognize that this "technical fix" would require costly tradeoffs and that it is therefore
probably not feasible.
You might also like to view...
If the force on a body is halved then the acceleration of the body
a. increases by half b. increases by double c. decreases by half d. decreases by double
Rotational Kinetic Energy: A solid uniform disk is rolling without slipping along a horizontal surface with a speed of 4.5 m/s when it starts up a ramp that makes an angle of 25° with the horizontal. What is the speed of the disk after it has rolled 3.0 m up as measured along the surface of the ramp?
A. 4.0 m/s B. 1.9 m/s C. 2.1 m/s D. 6.8 m/s E. 8.0 m/s
A 60.0-kg person drops from rest a distance of 1.20 m to a platform of negligible mass supported by an ideal stiff spring of negligible mass. The platform drops 6.00 cm before the person comes to rest
What is the spring constant of the spring? A) 2.56 × 105 N/m B) 3.92 × 105 N/m C) 5.45 × 104 N/m D) 4.12 × 105 N/m E) 8.83 × 104 N/m
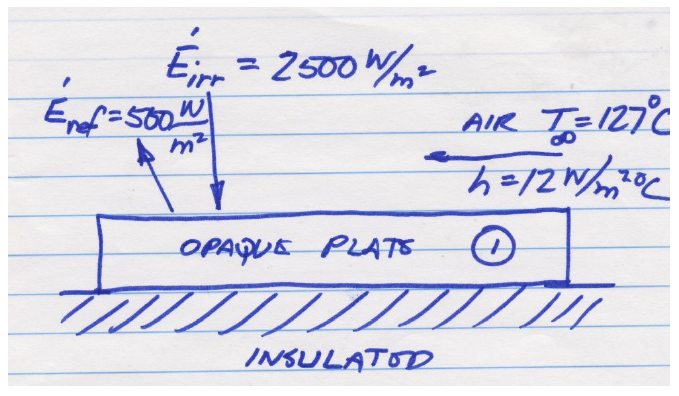
An opaque horizontal plate is insulated on the backside. The plate irradiation is 2500 W/m^2 of which 500 W/m^2 is reflected. The plate temperature is 227ºC and has an emissive power of 1200 W/m^2. Air at 127ºC and with a convective heat transfer coefficient of 12 W/m^2 K flows over the plate. Determine (a) emissivity, absorptivity, and radiosity of the plate and (b) the net heat transfer per unit area.