A lower price level causes
a. the entire aggregate expenditure to shift up.
b. the entire aggregate demand curve to shift to the right.
c. a movement along a given aggregate demand curve.
d. both a movement along a given aggregate demand curve and the entire aggregate expenditure to shift up.
d. both a movement along a given aggregate demand curve and the entire aggregate expenditure to shift up.
You might also like to view...
Using the simple Keynesian model with a consumption function of C = 200 + .9Y, an $10 change in desired investment leads to a change in equilibrium income of
A) $10. B) $100. C) $20. D) $90.
A speculator who believes strongly that interest rates will rise would be likely to
A) buy futures contracts on Treasury bills. B) sell futures contracts on Treasury bills. C) buy Treasury bonds in the spot market. D) increase now the amount of money which he lends.
If Slick Shades has a constant marginal cost of production equal to $40 and the distributors have a constant marginal cost of distribution equal to $20, what is the profit-maximizing number of sunglasses (in hundreds) for Slick Shades to produce?
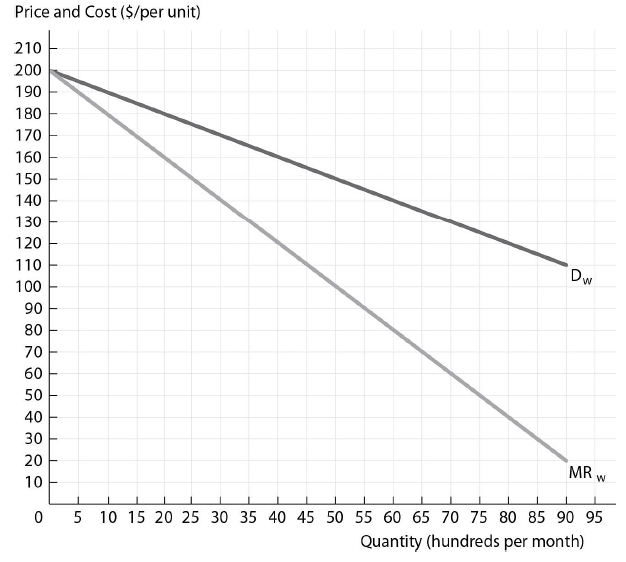
The figure above shows the wholesale demand and marginal revenue curves for Slick Shades Sunglasses, a sunglasses firm with market power. Slick Shades Sunglasses has a constant marginal cost of production and it sells to perfectly competitive independent retail distributors that have a constant marginal cost of distribution.
A) 90
B) 80
C) 50
D) 70
Sitting through a terrible movie till the end because you already bought the ticket is an example of:
A. making a decision at the margin. B. sunk cost fallacy C. negative utility endorsement. D. rational behavior.