The practice of dividing packages of debts into slices, each with different risk and return characteristics, is called:
A. leveraging.
B. bundling.
C. pooling.
D. tranching.
D. tranching.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. Player A can infer that Player B will: 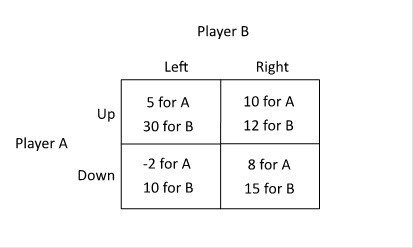
A. Player A cannot infer anything about what Player B will do given this matrix. B. choose Right. C. choose Left when A chooses Up and choose Right when A chooses Down. D. choose Left.
A progressive income tax is one that
A) taxes income so that the average tax rate decreases with the level of income. B) taxes all income above the guaranteed minimum at an average rate that decreases with income. C) taxes income so that the average tax rate increases with the level of income. D) taxes income at a constant rate, regardless of the level of income.
Suppose the working-age population of a fictional economy falls into the following categories: 90 are retired or homemakers; 60 have full-time employment; 20 have part-time employment; 20 do not have employment, but are actively looking for
employment; and 10 would like employment but do not have employment and are not actively looking for employment. The official unemployment rate as calculated by the U.S. Bureau of Labor would equal A) (20/80 ) × 100. B) (20/60 ) × 100. C) (30/80 ) × 100. D) (20/100 ) × 100.
The concepts of comparative advantage, specialization, and trade:
A. can be useful in explaining why countries import and export certain goods. B. can be useful in explaining why individuals typically work at one job, and buy the other goods and services they need. C. can be useful in explaining why we allow ourselves to be interdependent on others. D. All of the statements are true.