Explain the per-worker production function and its relationship to the catch-up effect. Give an example of how the catch-up effect works.
What will be an ideal response?
but students should demonstrate a thorough understanding of the per-worker function and how successive increases in capital per worker provide diminishing returns. This relates to the catch-up effect because it indicates that a capital investment in a poor country with little capital will boost output by a larger amount than the same investment in a country that already has adequate capital. For instance, investing $100 million in a port upgrade in the United States may make an already efficient port slightly more productive. Investing the same amount in a capital-poor country like Angola would enable a massive upgrade in port capacity and efficiency.
You might also like to view...
Refer to Scenario 14.4. Suppose that a tax is imposed on each unit of the product that John produces. Which curve will shift?
A) Marginal product of labor B) Marginal revenue product of labor C) The supply of labor D) All of the above will shift due to the tax on output.
In a capitalabundant country, free trade will cause a(n) __________ in the rental of capital and a(n) ____________ in the marginal product of capital.
a. increase; increase b. increase; decrease c. decrease; decrease d. decrease; increase
When the price is $5
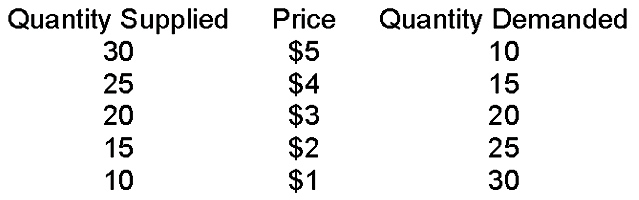
A. quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded and, therefore, price must rise to get to equilibrium.
B. quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded and, therefore, price must fall to get to equilibrium.
C. quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied and, therefore, price must rise to get to equilibrium.
D. quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied and, therefore, price must fall to get to equilibrium.
If entry is completely free, the demand curve for the leading, profit-making monopolistic competitor will
A. move to the right until where MC=MR is where the ATC curve is tangent to the demand curve. B. become steeper while moving to the right. C. move to the left until where MC=MR is where the ATC curve is tangent to the demand curve. D. move to the left until where MC=MR is where the AVC curve is tangent to the demand curve.