What is p the probability of?
a. p is the probability that the results are due to chance, the probability that the null hypothesis 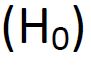 is true.
is true.
b. p is the probability of observing results as extreme as (or more extreme than) observed, if the null hypothesis 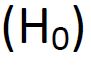 is true.
is true.
c. p is the probability that the results are not due to chance, the probability that
the null hypothesis 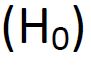 is false.
is false.
d. p is the probability that the results would be replicated if the experiment was conducted a second time.
b. p is the probability of observing results as extreme as (or more extreme than) observed, if the null hypothesis 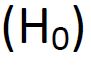 is true.
is true.
You might also like to view...
It used to be thought that all infants experienced sensations and environmental stimuli in similar ways, but now it is believed that infants
What will be an ideal response?
A central aspect of building students' creative literacy is to value their ideas and emotions.?
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Name and briefly describe 3 variations on standard group times as listed in your textbook.
What will be an ideal response?
Textbooks that students can become frustrated with are based on what percentage of recognizable words?
a. 95% or over b. 90% c. 100% d. 90% or less