Refer to the table. A decline in the international value of the dollar would:
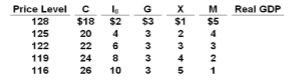
Answer the question on the basis of the following table for a particular country in which C is
consumption expenditures, I g is gross investment expenditures, G is government expenditures,
X is exports, and M is imports. All figures are in billions of dollars. Each question is
independent of other question using the same table, unless otherwise stated.
A. increase the values in columns (5) and (6) and reduce aggregate demand.
B. decrease the values in columns (5) and (6) and increase aggregate demand.
C. decrease the values in column (5), increase the values in column (6), and reduce
aggregate demand.
D. increase the values in column (5), decrease the values in column (6), and increase
aggregate demand.
D. increase the values in column (5), decrease the values in column (6), and increase
aggregate demand.
You might also like to view...
Supply-siders are generally critical of government intervention and regulation, since they believe regulations can be costly impediments to economic growth
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
In a barter economy,
A) money trades for goods, goods trade for services, and services trade for money. B) goods and services trade for other goods and services. C) some goods are more readily accepted in exchange than others. D) making exchanges takes less time (on average) than in a money economy. E) b and c
In most countries, decisions that affect medical expenditures are
A. centralized. B. decentralized. C. determined by government policy. D. both centralized and decentralized.
(Figure: Long-Run Aggregate Supply Curves) Which of the following can explain the shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve from A to C in the figure?
What will be an ideal response?