Solar radiation is incident on a 5-m2 solar absorber plate surface at a rate of 800?W/m2. Ninety-three percent of the solar radiation is absorbed by the absorber plate, while the remaining 7 percent is reflected away. The solar absorber plate has a surface temperature of 40°C with an emissivity of 0.9 that experiences radiation exchange with the surrounding temperature of ??5°C. In addition, convective heat transfer occurs between the absorber plate surface and the ambient air of 20°C with a convection heat transfer coefficient of 7?W/m2•K. Determine the efficiency of the solar absorber, which is defined as the ratio of the usable heat collected by the absorber to the incident solar radiation on the absorber.
What will be an ideal response?
A flat-plate solar absorber is exposed to an incident solar radiation. The efficiency of the solar absorber (the ratio of the usable heat collected by the absorber to the incident solar radiation on the absorber) is to be determined.
Assumptions 1 Steady operating conditions exist. 2 Temperature at the surface remained constant.
Properties The absorber surface has an absorptivity of 0.93 and an emissivity of 0.9.
Analysis The rate of usable heat at the absorber plate can be expressed as
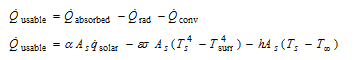
Expressed in terms of heat flux, we have
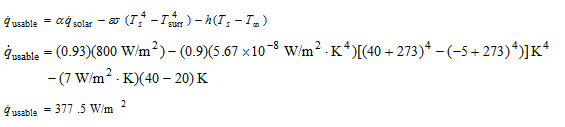
Thus, the efficiency of the solar absorber is
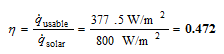
Discussion The efficiency of the solar absorber is influenced by the surrounding and ambient temperatures, as well as the convective heat transfer coefficient. If the weather is particularly windy, thus causing higher level of heat loss via convection, then the efficiency of the solar absorber could be adversely affected.
You might also like to view...
If a source file contains ____ errors, it cannot be converted into an executable file.
A. syntax B. debugging C. compilation D. logic
If the needle on the pressure gauge fluctuates erratically during a hydrostatic test, this indicates that _____
a. the pressure is too high b. the pressure is too low c. there is a leak d. there is air trapped in the system
How is the R value determined for a composite structure, such as a wall?
A) The R value of the component with the highest R value is used. B) The R value of the component with the lowest R value is used. C) The R values of all the individual components are added together and averaged. D) The R values of all the individual components are added together.
The charging scheme used in Figure P2.12 is called a tapered-current charge cycle. The current starts at the highest level and then decreases with time for the entire charge cycle, as shown. The battery is charged for 12 h. Find:
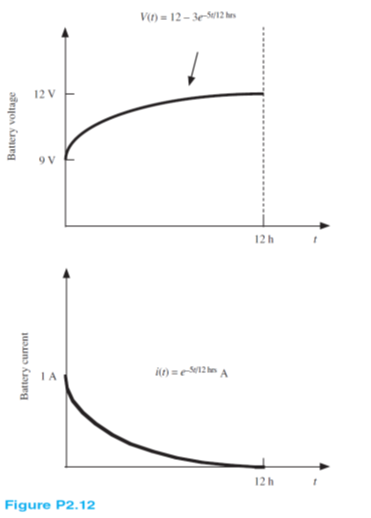
a. The total charge delivered to the battery.
b. The energy transferred to the battery during the charging cycle.
Hint: Recall that the energy, w, is the integral of power, or P = dw/dt.