Active transport ________.
A. cannot be saturated
B. cannot transport molecules against a concentration gradient
C. utilizes energy
D. requires cofactors
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
____________________ is the inability to prevent the discharge of urine
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
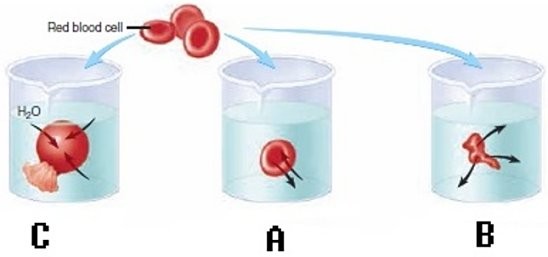 Red blood cells (RBCs) have been placed in three different solutions: hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic. What is solution "A" relative to the RBC?
Red blood cells (RBCs) have been placed in three different solutions: hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic. What is solution "A" relative to the RBC?
A. Isotonic solution B. Hypertonic solution C. Hypotonic solution
The relaxation phase of the lower chambers of the heart is called
A) ventricular systole. B) ventricular diastole. C) atrial systole. D) atrial diastole. E) None of the answers aer correct.
In the process of endochondral ossification, ________ is(are) replaced by bone.
A. hyaline cartilage B. fibrocartilage C. connective tissue membranes D. elastic cartilage