Suppose Firm A and Firm B are considering whether to invest in a new production technology. For each firm, the payoff to investing (given in thousands of dollars per day) depends upon whether the other firm invests, as shown in the payoff matrix below. 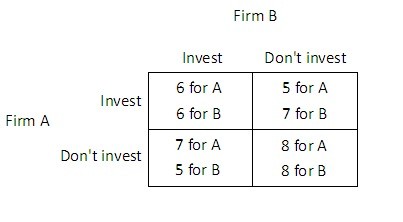 What is the Nash equilibrium of this game?
What is the Nash equilibrium of this game?
A. Firm A invests, and Firm B invests.
B. Firm A doesn't invest, and Firm B doesn't invest.
C. Firm A doesn't invest, and Firm B invests.
D. Firm A invests, and Firm B doesn't invest.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
When the price level increases people:
A. demand a smaller quantity of goods and services in the aggregate. B. feel more wealthy. C. have the same real value of assets, regardless of the change in the price level. D. want to spend more, but can’t due to the prices of all goods and services going up.
Which of the following statements best describes the belief among economists about trade?
a. The common belief among economists is that it is better to embrace the gains from trade, and then deal with the costs and trade-offs with other policy tools than it is to cut off trade to avoid the costs and trade-offs. b. The common belief among economists is that it is better to cut off trade to avoid the costs and trade-offs than it is to embrace the gains from trade and then deal with the costs and trade-offs with other policy tools. c. The common belief among economists is that it is better to deal with the costs and trade-offs of trade with other policy tools before embracing the gains from trade, than it is to cut off trade to avoid the costs and trade-offs. d. The common belief among economists is that it is better to cut off trade to avoid the costs and trade-offs, deal with the costs and trade-offs with other policy tools, and then embrace the gains from trade.
If greater equality is the benefit of government intervention into the allocation of society's resources, what is the cost?
Anna was willing to pay $130,000 for Betty’s house, which was listed at $125,000, but Anna could only afford to spend $120,000. After negotiating, Betty sold Anna the house for $120,000. How does consumer surplus apply to this situation?
a. The consumer surplus is indeterminable because we do not know how much Betty paid for the house. b. The consumer surplus is $5,000 because Anna got Betty to lower her price by that amount. c. The consumer surplus is $10,000 because Anna was willing to pay that much more than she did. d. There is no consumer surplus because Anna did not pay less than she was willing and able to pay.