In a disparate treatment case:
a. if the plaintiff meets the burden of proving a prima facie case, the burden of proof shifts to the employer.
b. an employer will not prevail in the face of a plaintiff's prima facie case unless it can articulate legitimate, non-discriminatory reasons for its actions.
c. if a plaintiff can show that a defendant's allegedly legitimate reason for not hiring plaintiff is merely a pretext for discrimination, the plaintiff wins.
d. All of these.
d
You might also like to view...
c. internal noise
a. external noise. b. a distraction. c. a noise channel. d. nonverbal communication.
Why are journals and ledgers not modeled in an REA diagram?
With cross-tabulation, two variables are arranged in a:
A) consistent and significant pattern B) cross-tabulation cell C) chi-square cell D) cross-tabulation table E) stacked bar table
Consider the data in problem 2 and perform a scenario analysis using the percentages of change for the same uncertain variables and the probabilities for each scenario given in the following table:
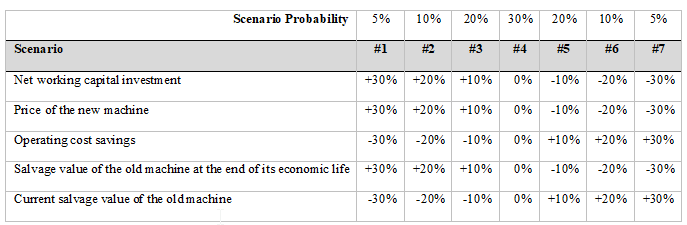
a) Determine the payback period, discounted payback period, NPV, PI, IRR, and MIRR of this project under each scenario.
b) Determine the expected NPV, PI, and IRR, and the corresponding standard deviation, coefficient of variation, and the probability of a negative NPV, a PI equal to 1, and an IRR equal to the firm’s IRR.
c) Perform a Monte Carlo simulation with 1,000 trials to determine the expected NPV. Also determine the standard deviation of the expected NPV. The uncertain variables and their probability distributions are given in the following table:
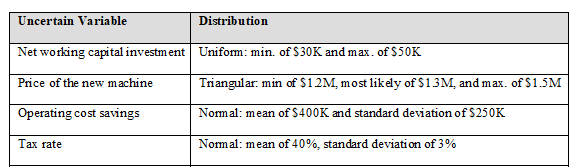
d) Create a histogram using the Histogram chart type, showing the probability distribution of NPV.
e) Using the output of the simulation, determine the probability that the NPV will be less than or equal to zero. Compare your results with those of part (a).