Explain the marginal revenue and marginal cost approach to profit maximization and use it to describe profit, loss, and shut down situations for the purely competitive firm
What will be an ideal response?
The purely competitive firm operating in the short run is a price taker that can maximize profits (or minimize losses) only by changing its level of output. The marginal revenue–marginal cost approach to profit maximization basically sets the level of output at the quantity where marginal revenue (or price) equals marginal cost. There are three possible cases to consider when using this approach. First, the firm will maximize profits when MR=MC at an output level where price is greater than average total cost. Second, the firm will minimize losses when MR=MC at that output level where price is greater than the minimum average variable cost (but less than average total cost). Third, the firm will shut down when MR=MC at an output level where price is less than average variable cost.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the table below. Suppose the profit for each unit of paper product is $2 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $5 and Big Oaks is producing the profit-maximizing quantity of lumber and paper products. If the profit from each unit of lumber increases from $5 to $6 and the profit for each unit of paper products does not change, to maximize profit, Big Oaks should produce a ________
proportion of lumber and produce ________ units of paper products and lumber.
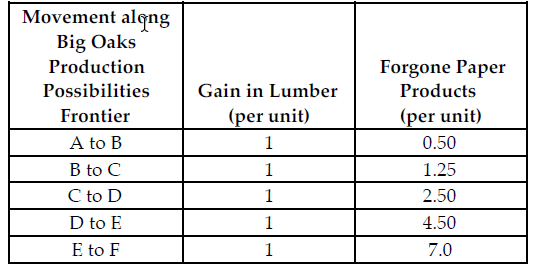
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amount of paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable proportions. The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
A) smaller; more
B) smaller; less
C) greater; less
D) greater; more
A tractor used to prepare land for planting is called
A) land. B) labor. C) physical capital. D) human capital.
A point inside the production possibilities curve represents a combination of goods that is
a. inefficient. b. efficient. c. unattainable. d. attainable.
The law of diminishing marginal returns states:
a) As a firm uses more of a variable factor of production, with a given quantity of the fixed factor of production, the marginal product of the variable factor eventually diminishes. b) As a firm uses more of a variable factor or production, total product eventually decreases. c) As the size of a firm?s plant increases, average cost eventually decreases. d) As the size of a plant increases, marginal product eventually decreases. e) As a firm uses more of a variable factor of production, its average cost eventually decreases.