How can regional concentration of firms in an industry lead to external economies of scale? Give examples of these types of industrial clusters in the United States. Are they always beneficial?
What will be an ideal response?
When an industry is highly concentrated in a specific location, this leads to a decrease in costs for firms that are located there regardless of their individual size. Close physical proximity enhances knowledge spillovers that keep all firms abreast of the latest technology and newest developments. Information can be exchanged through both formal and informal networks, and this is particularly important in frontier industries undergoing rapid technological change. Labor markets deepen for highly specialized skills, which reduces search costs and gives firms a choice of workers with the best skills. Dense networks of highly specialized input suppliers can also develop. All of these function to enhance production and to reduce costs. Hollywood, Silicon Valley, Nashville, and many other examples of industrial concentration exist in the United States. A potential problem for world trade is that an industrial cluster may develop and prevent potentially more efficient foreign producers from entering a market. These regional concentrations become self-reinforcing. Small initial differences in costs lead to feedback mechanisms that create large differences in costs based on production location. Hypothetically, a region could get an early advantage, form an agglomeration, and the cost advantages may prevent the development of the industry in another location that could have been more efficient. Production is thus concentrated with the less efficient producer because the more efficient producer never has the chance to get off the ground.
You might also like to view...
If a monopoly can perfectly price discriminate, then its marginal revenue curve will be
A) the same as its demand curve. B) the same as its supply curve. C) the same as its marginal cost curve. D) a vertical line at the profit-maximizing quantity of output. E) undefined because it does not exist.
Any market that we are studying and the markets for the related inputs must all be in equilibrium at the same time. This leads to:
A. simultaneous equilibrium effects. B. partial equilibrium effects. C. general equilibrium effects. D. equilibrium-induced changes.
If the prevailing price of shirts is $10 and at this price demanders demand 100 shirts while suppliers are willing to supply 110 shirts, there is a(n)
a. shortage at the $10 price. b. surplus at the $10 price. c. equilibrium in this market. d. shortage if price were to rise above $10.
The increase in the price of sugar created by the tariff will lead domestic production to increase by ________ tons per year, compared to when the economy is open without the tariff.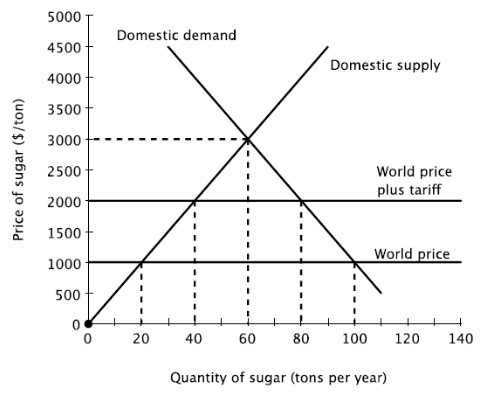
A. 10 B. 20 C. 40 D. 30