Matching. Choose the most appropriate response for each. 1. ___ age structure 2. ___ population growth rate 3. ___ J-shaped curve 4. ___ limiting factor A. describes a population that is experiencing unrestrained growth B. the
birth rate minus the death rate plus any
inward migration and minus any outward
migration
C. the distribution of individuals at each age
level in a population
D. for example, the amount of glucose in a
culture flask containing bacteria
Answers: 1. C, 2. B, 3. A, 4. D
You might also like to view...
Of the following, the best way to separate the effects of genes and environment in research is to study
a. identical twins b. adopted children and their adoptive parents c. fraternal twins d. identical twins raised in different environments
A group of turtles is washed ashore on an island and no longer breeds with any turtles other than those on the island. After centuries of isolation, they no longer interbreed with the original species
This situation is best described by the term: A. allopatric speciation. B. migration. C. phylogenetic speciation. D. genetic drift. E. natural selection.
Refer to Figure 5-1. Which of the following statements about the red blood cells in Figure B is true?
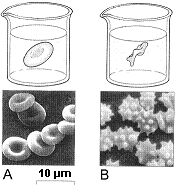
a. These red blood cells have been placed in an isotonic solution.
b. These red blood cells have swollen in response to a hypertonic external solution.
c. These red blood cells have swollen in response to a hypotonic external solution.
d. These red blood cells have shrunken in response to a hypertonic external solution.
e. These red blood cells have shrunken in response to a hypotonic external solution
Which of the following does NOT accurately apply to the Ames test?
a. The test uses bacteria as mutagen carcinogen indicators. b. The Ames test is based on the observation that reversions CANNOT occur in mutant bacteria. c. The Ames test measures the reversion of histidine auxotrophs of Salmonella. d. The test can be used to qualitatively test potential mutagens.