A price-taker faces a demand curve that is:
A. upward sloping.
B. horizontal at the market price.
C. downward sloping.
D. vertical at the market price.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
When a firm’s AC eventually starts to rise, it is often because
A. executive salaries rise sharply as output rises. B. the ability to manage larger and larger levels of output results in much higher administrative costs. C. marginal cost increases rapidly at higher output levels. D. firm output has started to decline.
Darryl can build picnic tables twice as fast as Trevon. Darryl can assemble swing sets three times as fast as Trevon. The law of comparative advantage suggests that
a. Darryl can gain only at Trevon's expense. b. Trevon can gain only at Darryl's expense. c. both can gain if Darryl specializes in assembling swing sets and Trevon in building picnic tables. d. both can gain if Darryl specializes in building picnic tables and Trevon in assembling swing sets.
As shown in Exhibit 3, ______ has ______ in producing both cloth and food.
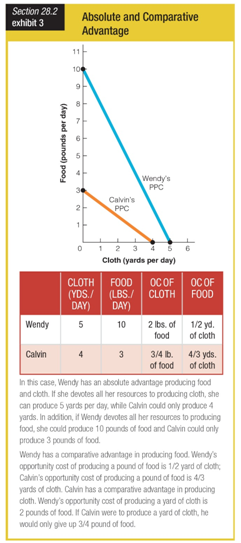
a. Calvin; an absolute advantage
b. Calvin; a comparative advantage
c. Wendy; an absolute advantage
d. Wendy; a comparative advantage
At the intersection of the short-run aggregate supply curve, the aggregate demand curve, and the long-run aggregate supply curve, the economy is in:
A. neither a short-run nor long-run equilibrium. B. a short-run equilibrium but not a long-run equilibrium. C. both a short-run and long-run equilibrium. D. a long-run equilibrium but not a short-run equilibrium.