Considering the information in the table shown, if Jack decides to consume bundle D, we can conclude that Jack:
This table shows the different combinations of goods that Jack can consume, given that his income to spend on these two items is $10.
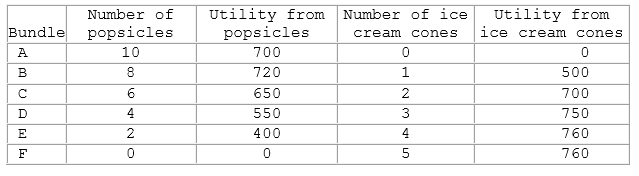
A. still has money left to spend.
B. is not maximizing his utility.
C. could consume more of both goods.
D. All of these are true.
B. is not maximizing his utility.
You might also like to view...
The opportunity cost of increased production of some good can be measured with
A. the slope of a ray to the production possibilities curve. B. the area under the curve of a production possibilities curve. C. the area of the rectangle bounded by the axes and the point on the production possibilities curve. D. the slope of the production possibilities curve. E. All of the responses are correct.
The above figure shows Bob's utility function. He currently has $100 of wealth, but there is a 50% chance that it could all be stolen. Bob will buy theft insurance to cover the full $100
A) as long as it does not cost more than $25. B) as long as it does not cost more than $50. C) as long as it does not cost more than $70. D) at any price.
If on Tuesday you can buy 125 yen per U.S. dollar and on Wednesday you can buy 120 yen per U.S. dollar,
a. both the U.S. dollar and the yen have appreciated b. both the U.S. dollar and the yen have depreciated c. the U.S. dollar has appreciated and the yen has depreciated d. the U.S. dollar has depreciated and the yen has appreciated e. the yen has appreciated and the U.S. dollar has remained constant
If a firm in a perfectly competitive market is currently producing the output where price = marginal cost = average total cost, the firm is:
A. earning a positive economic profit. B. earning a zero economic profit. C. suffering an economic loss. D. All of these