For any given output level, a firm's long-run costs
a. are always greater than or equal to its short-run costs.
b. are usually greater than or equal to its short-run costs except in the case of diminishing returns to scale.
c. are always less than or equal to its short-run costs.
d. are usually less than or equal to its short-run costs except in the case of diminishing returns to scale.
c
You might also like to view...
In L. Frank Baum's classic 1900 children's book, The Wonderful Wizard of Oz, the name "oz" is a reference to
A) an ounce (oz.) of gold. B) an ounce (oz.) of silver. C) an ounce (oz.) of copper. D) an ounce (oz.) of gold or silver. E) an ounce (oz.) of wheat.
People who are in the process of changing jobs are counted as
A. frictionally unemployed. B. underemployed. C. structurally unemployed. D. cyclically unemployed.
YearAntonio's Hourly wageConsumer Price Index2006$8.40201.62010$9.05218.1 Refer to Table 8.2. From 2006 to 2010, Antonio received a total of $0.65 in pay raises, and the CPI also increased as shown in the table. What happened to Antonio's real wage from 2006 to 2010?
A. It rose because Antonio's nominal wage and the CPI were both higher in 2010 than in 2006. B. It fell because Antonio's nominal wage rose more slowly than did the CPI. C. It rose because $9.05 is greater than $8.40. D. It fell because the change in the CPI was 16.5, which is greater than Antonio's wage.
The firm's most efficient output would be
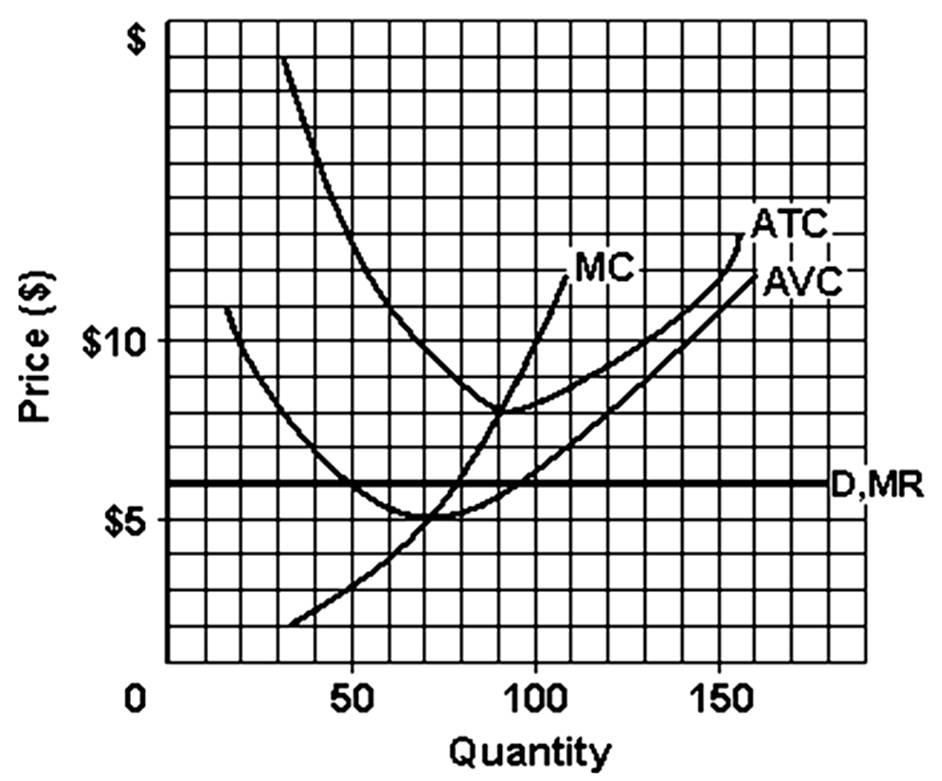
A. 70 units.
B. 80 units.
C. 90 units.
D. 100 units.