The difference between a private good and a public good is that
A) private goods are government-sponsored goods while public goods are government-inhibited goods.
B) externalities are always created in the production process but not in the production of public goods.
C) private goods make us happy while public goods do not.
D) the exclusion principle applies to a private good but not to a public good.
D
You might also like to view...
The observation that consumer purchases of walnuts decline as the price rises reflects:
a. a decrease in demand. b. the law of demand. c. an increase in demand. d. the law of supply.
Natural monopoly exists when
a. marginal costs are less than average costs for all output levels b. average costs are less than marginal costs for all output levels c. profit is impossible for a private firm d. efficient production is impossible for a private firm e. none of the above
Figure 6-1
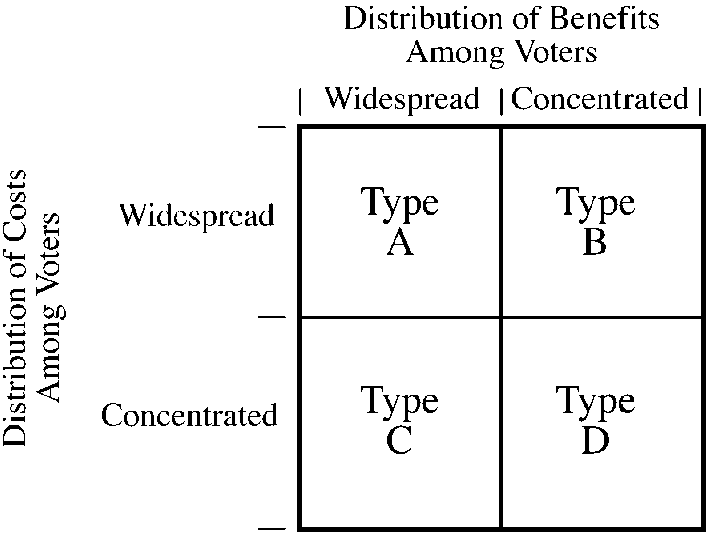
illustrates the four possibilities of the distribution of costs and benefits among voters for a government project. Programs that give subsidies to a small group of producers at general taxpayer expense would be considered
a.
type A projects, and the government would be likely to undertake these projects if they were efficient and to reject them if they were inefficient.
b.
type B projects, and the government would be likely to undertake many of these projects even when they were counterproductive (inefficient).
c.
type C projects, and the government would be likely to fail to undertake many of these projects even when they were productive (efficient).
d.
type D projects, and the government would be likely to undertake these projects if they were efficient and to reject them if they were inefficient.
If the price of an input increases, each individual firm's marginal cost curve shifts ________ and the industry supply curve ________.
A. downward; shifts to the right B. up; does not change C. downward; shifts to the left D. up; shifts to the left