Personal income is
A) equal to GDP.
B) that portion of national income that can be used for consumption and saving.
C) the sum of all payments to suppliers of the factors of production.
D) the amount of income that individuals actually receive.
E) another term for disposable income.
D
You might also like to view...
The table above gives the demand schedule for peas. Between point A and point B, the price elasticity of demand equals
A) 0.11. B) 0.50. C) 0.22. D) 9.09.
The IMF's approach to structural adjustment usually
a. placed priority on growth-related investments b. eased conditions by providing subsidies for goods consumed by the poor c. aimed to switch production from goods consumed domestically to goods intended for export d. focused on governments switching expenditure from defense spending to job creation e. all of the above
When countries converge,
A) they all grow at the same rate. B) poorer ones grow faster. C) richer ones grow faster. D) richer ones do not grow.
Refer to the table below. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $2 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $5, what is Big Oaks' marginal cost of producing between points D and E on their production possibilities frontier?
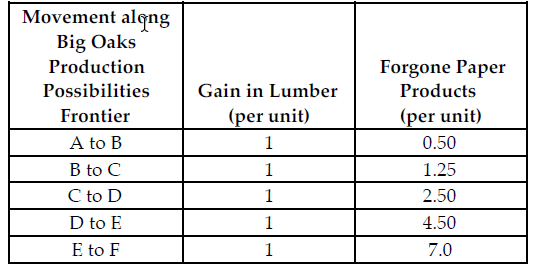
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amount of paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable proportions. The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
A) $22.50
B) $4.50
C) $9
D) $10.50