In the fooling model's labor market diagram, from an initial intersection point of the labor supply and demand curves, tracing "northeast" up the labor supply curve shows
A) what happens to real wages and employment when aggregate demand expands.
B) what happens to real wages and employment when aggregate demand contracts.
C) what workers think is happening to real wages if an aggregate demand expansion fools them.
D) what firms think is happening to real wages if an aggregate demand expansion fools them.
C
You might also like to view...
Explain the impact of capital deepening on workers
What will be an ideal response?
When an economist uses the term "cost" referring to a firm, the economist refers to the
A) price of the good to the consumer. B) explicit cost of producing a good or service but not the implicit cost of producing a good or service. C) implicit cost of producing a good or service but not the explicit cost of producing a good or service. D) opportunity cost of producing a good or service, which includes both implicit and explicit cost. E) cost that can be actually verified and measured.
Which of the following is a tax on consumption?
a. A comprehensive general sales tax. b. A comprehensive value-added tax c. An income tax in a world without saving. d. All of the above. e. a and b
The Lorenz curve showing perfect income equality would be
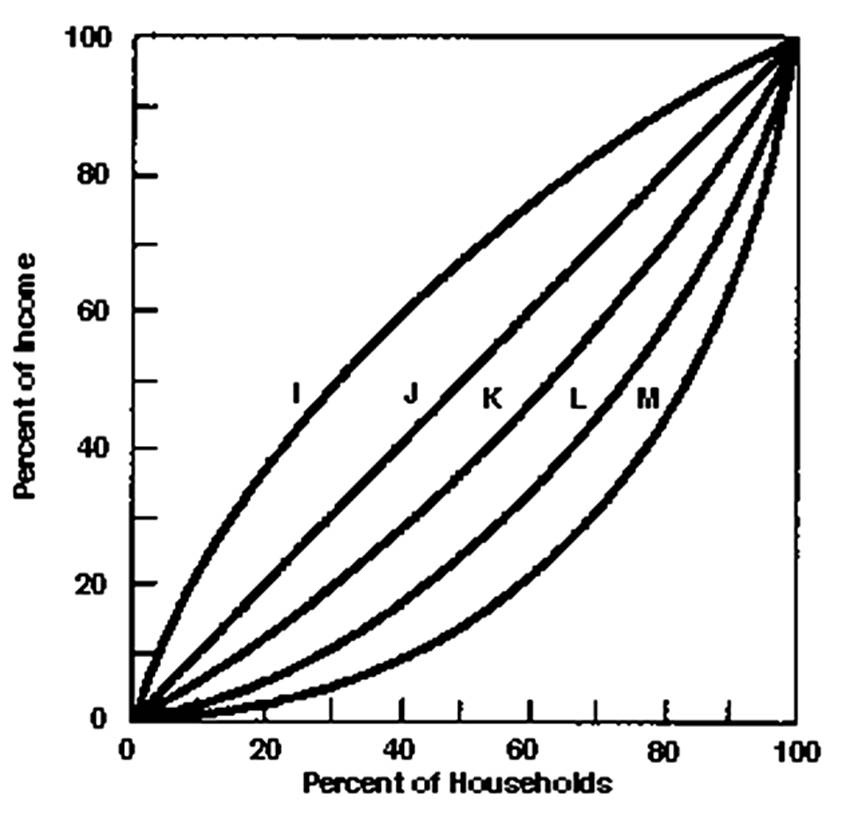
A. I.
B. J.
C. K.
D. L.