After a supernova event occurring in a high-mass star, what is left behind?
A) always a white dwarf
B) always a black hole
C) always a neutron star
D) either a white dwarf or a neutron star
E) either a neutron star or a black hole
E
You might also like to view...
A ball of mass 3m at speed v approaches a ball of mass 2m at speed -2v and they are about to collide. After the collision, what is the speed of the center of mass?
A. v B. -v/5 C. v/5 D. -v E. Can't decide because we don't know whether this collision is inelastic or elastic
As you’ve learned from Part B, hydrogen and helium gas never condense under conditions found in the solar nebula. The remaining three categories of material in the solar nebula are shown again here. Rank these materials from left to right based on the distance from the Sun at which they could condense into a solid in the solar nebula, from farthest to closest.
What will be an ideal response?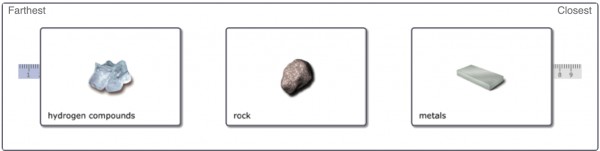
A concave mirror with a radius of 20 cm creates a real image 30 cm from the mirror. What is the object distance?
A) 50 cm B) 20 cm C) 15 cm D) 7.5 cm E) 5.0 cm
An object that has zero resistance is a semiconductor
Indicate whether the statement is true or false