Peter was recently hired as a salesman for a national consulting firm. His job involves spending a significant portion of his time out of the office visiting prospects and attending conferences. His firm is paying him a wage that is higher than the equilibrium wage, but he receives much of his income in quarterly bonuses based on how much he sells
a. The consulting firm is trying to prevent adverse selection with its compensation strategy.
b. Peter has an incentive to go golfing with his buddies rather than conducting sales meetings.
c. The consulting firm is responding to the moral hazard problem with its compensation strategy.
d. Peter should quit this job and take a job where he gets paid an equilibrium wage more frequently.
c
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 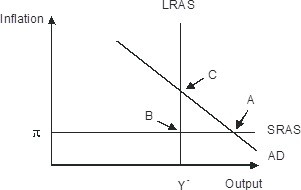
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
In most business situations where firms compete, often they can escape the prisoner's dilemma and reach the most profitable outcome. Which of the following is a reason for this?
A) Most games are repeated games and firms can employ retaliation strategies against those who do not cooperate. B) Most games are one-shot games so firms learn from their mistakes. C) Firms are constantly improving their products and anticipating changing consumer tastes. D) Firms engage in aggressive advertising to overcome the barriers to loyalty.
The difference in the selling and purchase prices of government securities in a typical overnight repurchase agreement is set to reflect
A) the difference in the auction price of the securities and their current market price. B) the overnight cost of funds. C) LIBOR. D) the discount on Treasury bills.
To maximize its profit, a monopoly should choose a price where demand is:
A. elastic. B. inelastic. C. unitary elastic. D. vertical.