In contrast to American firms, Japanese firms frequently make lifetime employment commitments to their workers and agree not to lay them off when product demand is weak. Other things being equal, we would expect Japanese firms to:
A. face more elastic product demand curves than American firms.
B. have relatively greater variable costs than American firms.
C. discontinue production at higher product prices than would American firms.
D. continue to produce in the short run at lower prices than would American firms.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is true?
a. More than half of medical bills are paid for directly by consumers. b. Healthcare insurance provided by one's employer is counted as personal income. c. State mandated coverage of medical procedures like in-vitro fertilization, drug rehabilitation, and acupuncture, make health insurance more affordable. d. Regulations prevent consumers from purchasing a health insurance plan offered in another state.
Which of the following is NOT a financial intermediary?
A. a savings and loan association B. commercial banks C. the Internal Revenue Service D. the Federal Reserve Bank of New York
Refer to the information provided in Figure 14.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow.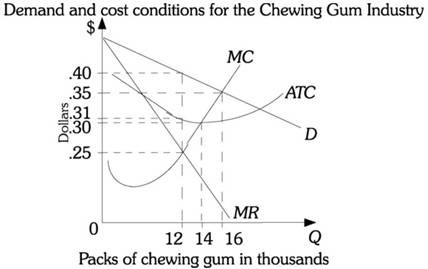 Figure 14.1Refer to Figure 14.1. Four chewing gum producing firms form a cartel. The firms have identical cost structures. If the cartel produces the profit-maximizing output level, each firm should produce
Figure 14.1Refer to Figure 14.1. Four chewing gum producing firms form a cartel. The firms have identical cost structures. If the cartel produces the profit-maximizing output level, each firm should produce
A. 3,000 packs of chewing gum. B. 4,000 packs of chewing gum. C. 12,000 packs of chewing gum. D. indeterminate output levels from this information.
The slope of the monetary policy reaction curve is determined by:
A. how strongly the economy reacts to changes in the nominal interest rate. B. how strongly the inflation rate impacts peoples' decisions. C. people's expectations for inflation. D. how aggressively policymakers change interest rates in response to deviations between current and target inflation rates.