What was the GATT, why was it established, and why and with what was it replaced?
What will be an ideal response?
By the end of World War II in 1945, government officials in the United States and Europe were looking for a way to reduce tariffs and revive international trade. To help achieve this goal, they set up the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) in 1948. Countries that joined GATT agreed not to impose new tariffs or import quotas. In the 1940s, most international trade was in goods, and the GATT agreement covered only goods. In the following decades, trade in services and products incorporating intellectual property, such as software programs and movies, grew in importance. Many GATT members pressed for a new agreement that would cover services and intellectual property, as well as goods. A new agreement was negotiated, and in January 1995, the GATT was replaced by the World Trade Organization (WTO).
You might also like to view...
In the long run, the key reason that money is neutral is that
A) the federal budget is balanced. B) prices are flexible. C) business cycles have become much milder. D) the nominal interest rate must equal the real interest rate.
Which of the following is the most likely explanation of Japan's very low market interest rates in the early 2000s?
A) expected deflation B) an increasing budget deficit C) an increasing trade surplus D) an increase in corporate profits
Refer to Table 4-4. If a minimum wage of $9.50 is mandated there will be a
A) shortage of 20,000 units of labor.
B) surplus of 10,000 units of labor.
C) shortage of 10,000 units of labor.
D) surplus of 20,000 units of labor.
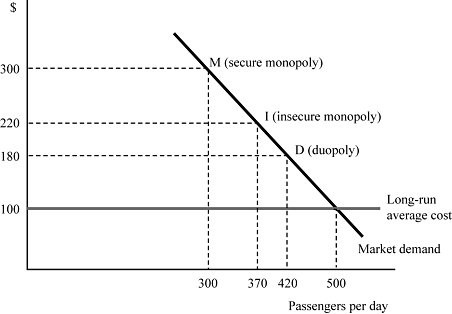
 In Figure 8.10, airline Fly Smart is initially a secure monopoly between two cities X and Y at point M, serving 300 passengers per day at the profit-maximizing price of $300 per ticket. Suppose that Fly Smart discovers that a second airline is contemplating entering the market. If the minimum market entry quantity is 130 passengers per day, Fly Smart's entry-deterring quantity is:
In Figure 8.10, airline Fly Smart is initially a secure monopoly between two cities X and Y at point M, serving 300 passengers per day at the profit-maximizing price of $300 per ticket. Suppose that Fly Smart discovers that a second airline is contemplating entering the market. If the minimum market entry quantity is 130 passengers per day, Fly Smart's entry-deterring quantity is:
A. 500 passengers per day. B. 420 passengers per day. C. 370 passengers per day. D. 300 passengers per day.