Magnesium is the metal in a molar solution of Mg2+ ions with a reference electrode.
(a) What reactions take place at the electrodes?
(b) What voltage is developed in the standard cell?
(c) Calculate the Gibbs free energy change when 1 mole of magnesium dissolves into a standard solution through the reaction Mg?2e– + Mg2+ with a standard-reference electrode.
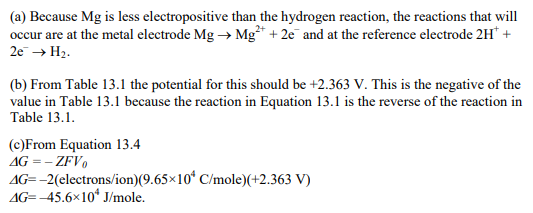
You might also like to view...
The dwarf planet Pluto and its moon Charon are unique in the Solar Systems in that the orbital period of Charon equals the rotation period of Pluto. The synchronous rotation is the result of tidal interaction between them.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
A point charge Q is placed on the x axis at the origin. An identical point charge is placed on the x axis at x = ?1.0 m and another at x = +1.0 m. If Q = 40 ?C, what is the magnitude of the electrostatic force on the charge at x = +1.0 m?
a. 29 N b. 14 N c. 11 N d. 18 N e. 7.0 N
A flat coil containing 25 identical loops carries 6.4 A of current. When it is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.22 T that is oriented parallel to the plane of the coil, the magnetic torque on it is 3.7 N ? m
(a) What is the magnetic moment of the coil? (b) What is the area of each loop?
An electric field is set up between two parallel plates, each of area 2.0 m2, by putting 1.0 ?C charge on one plate and a -1.0 ?C charge on the other. The plates are separated by 4.0 mm
What is the magnitude of the electric field between the plates at a distance of 1.0 mm from the positive plate? A) 4.2 × 104 N/C B) 1.4 × 104 N/C C) 3.1 × 104 N/C D) 0 N/C E) 5.6 × 104 N/C