One mole of an ideal gas with 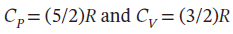 expands from
expands from 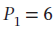 and
and 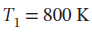 to
to 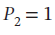 bar by each of the following paths:
bar by each of the following paths:
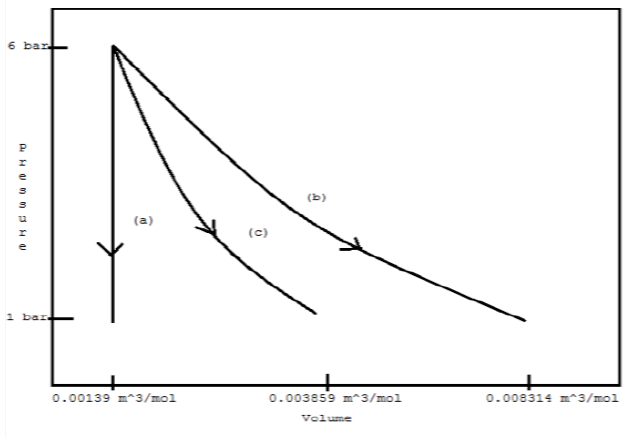
(a) Constant volume
(b) Constant temperature
(c) Adiabatically
Assuming mechanical reversibility, calculate W, Q, ?U, and ?H for each process. Sketch each path on a single PV diagram.
For each of these problems start with equations 3.13b, 3.14b, 3.16, and 3.17:
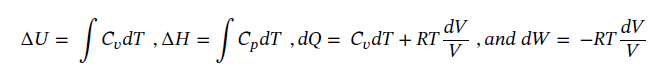
(a) at constant volume,
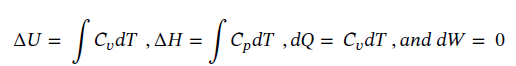
So plugging the given values into each part gives:
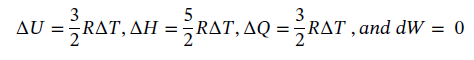
Now not knowing what T2 is, we must assume to stay at an ideal gas that since the pressure drops by a factor of 6, the temperature must drop by the same as well, leaving T2 = 800/6 = 133.33 K. Using this value gives the following values:
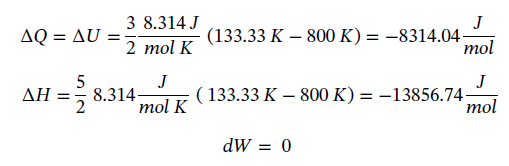
(b) Using the same starting point as in part (a) and assuming constant temperature, reduces the equations to the following:
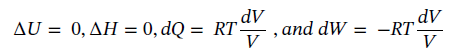
Putting in the known values and solving gives
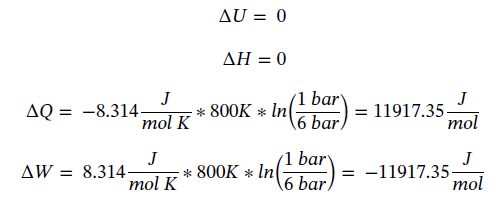
(c) Again starting with the same equations as in part (a) and assume dQ = 0 (adiabatic) gives:
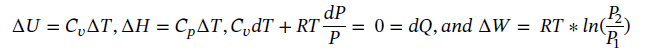
However, we also have adiabatic expansion which changes T2. Taking Eqn 3.16 integrating and solving for T2 gives:
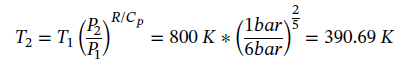
Plugging in given values and solving gives:
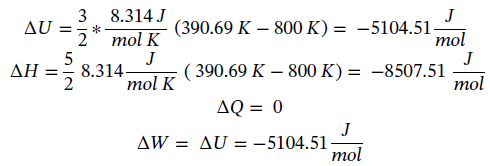
You might also like to view...
Another factor that can have a significant influence upon the discount rate used in life-cycle costing is the expected rate of ____.
A. inflation B. depreciation C. appreciation D. devaluation
Describe when tempered water might be supplied to public lavatory faucets.
What will be an ideal response?
Technician Asays air core electromagnetic gauges and quartz swing needle displays are similar. Technician B says in quartz needle displays, the A coil is connected to the system voltage and the B coil receives a voltage proportional to input frequency. Who is correct?
A. Technician A only B. Technician B only C. Both Technician A and B D. Neither Technician A nor B
"Breakdown voltage" is the voltage at which a Zener diode will do which of these?
A) Sustain damage as a result of current overload B) Allow reverse current to flow C) Stop the flow of reverse current D) Stop the flow of either forward or reverse current